The Comprehensive Guide to Real Estate Installment Sales
An installment obligation is considered to be property and is subject to valuation, as provided in paragraph (d)(2) (ii) and (iii) of this section, without regard to whether the obligation is embodied in a note, an executory contract, or any other instrument, or is an oral promise enforceable under local law. The term “gross profit” means the selling price less the adjusted basis as defined in section 1011 and the regulations thereunder. Such additions to basis will not be deemed to affect the taxpayer’s holding period in the transferred property.
Keep Capital Gains Taxed at 15%
Depending on whether the seller is an investor or a dealer, different requirements and considerations may be involved in calculating the gross profit and determining how selling expenses are handled. To qualify under the installment method, the otherwise eligible installment sale must produce a gain. Any losses arising from an installment sale are recognized in the year of sale—even if the sales price is paid over a number of years.
Example: Calculating New Gross Profit Percentage after Reducing Selling Price
On the other hand, deferred payments might be more suitable for sellers who prefer to defer tax liability to a future year, potentially taking advantage of lower tax rates or other favorable tax conditions. Understanding the nuances of each method is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with the seller’s financial goals and tax planning strategy. Interest plays a significant role in installment sales, often serving as a crucial component of the overall financial arrangement.
What is the difference between installment and payment?
For the buyer, installment purchases provide an opportunity to build equity in the property over time as they make payments. With each payment, the buyer’s equity in the property increases, eventually leading to full ownership upon completion of payments. For the buyer, there is the risk of defaulting on payments, which could result in the loss of partial ownership and any payments made up to that point. For the seller, there’s a risk of non-payment and having to repossess the property, which can be time-consuming and costly.
However, the seller may choose to report the entire gain when sold if either tax rates or their tax bracket is expected to be higher within the term of the installment payments. However, the installment sale method cannot be used for personal property sold at a loss. In the realm of real estate and asset transactions, installment sales have emerged as a powerful creative financing tool for sellers and buyers alike. In an installment sale contract — sometimes called a contract for deed — generally the owner agrees to sell the real estate to the buyer for periodic payments to be applied to the purchase price in some fashion. This financial arrangement allows sellers to defer tax liabilities and offers buyers flexible payment options. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of installment sales, exploring their mechanics, advantages, and potential pitfalls.
Determining the gross profit percentage is a fundamental step in managing an installment sale. This percentage represents the ratio of gross profit to the total contract price and is essential for calculating the taxable portion of each installment payment. To begin, gross profit is calculated by subtracting the seller’s adjusted basis in the property from the selling price.
How The Installment Sales Method Works
- In an installment purchase, the buyer may not need traditional bank financing to acquire the property fully.
- The installment sale method also does not apply if all installment payments are made in the same tax year.
- This document contains examples and solutions to computational problems involving the installment sales method.
- If the buyer is not able to fulfill the installment payment, they will be forced to return the property back to the seller.
- The installment method of reporting taxes was enacted by Congress so that taxpayers can pay taxes on the sale or other disposition of property over time, when the payments from an installment sale are received.
However, the seller typically retains a security interest in the property until the debt is fully satisfied. This in not like a lease option where the owner retains ownership until the purchase contract is triggered. Whether an obligation is convertible at a substantial discount depends upon the particular facts and circumstances. Also, if a privilege to convert an obligation into stock or an obligation which is readily tradable in an established securities market may not be exercised within a period of one year from the date the obligation is issued, a substantial discount shall be considered to exist.
If the property sold was depreciable, the portion of the gain attributable to depreciation must be reported as ordinary income in the year of sale, regardless of the installment method. This can significantly impact the tax liability in the first year and should be carefully planned for. Let’s look at John’s installment sale structure if he wants to defer capital gains taxes to a future calendar year. John now has $200,000 (between $400,000 and $200,000) in taxable gains to declare.
This allows the tax liability to be spread over several years (if the installment payments are to be spread out that long). An installment sale is a property sale in which at least one payment is not made after the tax year. Publication 537 explains that the Internal Revenue Service allows taxpayers the option to defer a portion of the gain from the sale of investment property through an installment sale agreement. This arrangement allows sellers the ability to defer a portion of their capital gain for several years. The seller can also opt out of the installment sales method for reporting again.
When selling a property through an installment sale, it is vital to understand how the gross profit is calculated. The gross profit is the difference between the selling price and the seller’s adjusted basis, as well as any additional factors that may be involved. For example, if the seller is not a dealer, they may also need to add selling expenses and any recapture income under Sections 1245 and 1250 of the Code. Short term capital gains, capital gains from pre-1996 installment sales, and all capital gains from the sale of collectibles must be reported on Schedule B, Part 2.
- We are a Sacramento real estate solutions and investment firm that specializes in helping homeowners sell burdensome houses fast, for cash.
- Properly accounting for interest ensures that the seller does not inadvertently underreport income, which could trigger penalties and interest from the IRS.
- It provides formulas for calculating selling price, contract price, initial payment, gross profit, income to report, and taxes due.
- With recurring invoices, businesses can set up automatic reminders for customers to make monthly installments.
- This article will discuss the three methods—installment, closed transaction, and open transaction—available to taxpayers for reporting sales that involve contingent consideration potentially payable outside the year of the sale.
The real estate consultant can also build out an asset strategy to improve the client’s real estate portfolio. Installment purchases in real estate in Nevada are generally governed by contract law, and the terms are outlined in the purchase agreement between the buyer and seller. Compliance with Nevada laws and regulations, as well as professional advice, is essential to ensure a smooth and successful installment purchase transaction.
Installment Sales Method (Income Taxation
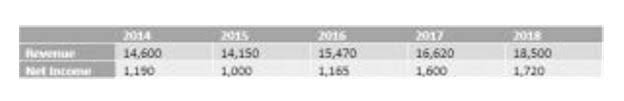
If the minimum interest is not charged, part of the sale price will be treated as imputed interest. Using the information provided in the table below, calculate your annual gain, not including interest. Installment payments are a prevalent method for dividing significant expenses into small and periodic payments, thus making them more manageable. The provisions of this paragraph (e) Installment Sales Method shall apply to sales or other dispositions occurring after May 27, 1969, which are not made pursuant to a binding written contract entered into on or before such date. No inference shall be drawn from this section as to any questions of law concerning the application of section 453 to sales or other dispositions occurring on or before May 27, 1969.