It is considered an asset because it represents a future economic benefit—the right to use the property for the period already paid for. As each day or month of the prepaid period passes, a portion of this prepaid asset is then transferred and recognized as a rent expense. Current liabilities are usually paid with current assets; i.e. the money in the company’s checking account. A company’s working capital is the difference between its current assets and current liabilities. Managing short-term debt and having adequate working capital is vital to a company’s long-term success. Having a better understanding of liabilities in accounting can help you make informed decisions about how to spend money within your company or organization.
- On the other hand, expenses directly affect profits—especially when operating costs increase.
- The company knows the exact amount of payment to be paid and actually incurred in the salaries payable.
- Usually, it comes to form the timesheets or other internal records within a company.
- A liability is generally an obligation between one party and another that’s not yet completed or paid.
- All liabilities are presented on the balance sheet, a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
- This occurs when an insurance premium is due to the insurer but remains unpaid.
Accrued Expenses vs. Prepaid Expenses
Many first-time entrepreneurs are wary of debt, but for a business, having manageable debt has benefits as long as you don’t exceed your limits. Read on to learn more about the importance of liabilities, the different types, and their placement on your balance sheet. Liabilities are a vital aspect of a company because they’re used to finance operations and pay for large expansions. They can also make transactions between businesses more efficient. A wine supplier typically doesn’t demand payment when it sells a case of wine to a restaurant and delivers the goods. It invoices the restaurant for the purchase to streamline the accounting drop-off and make paying easier for the restaurant.
What Are Proprietary Funds in Government Accounting?
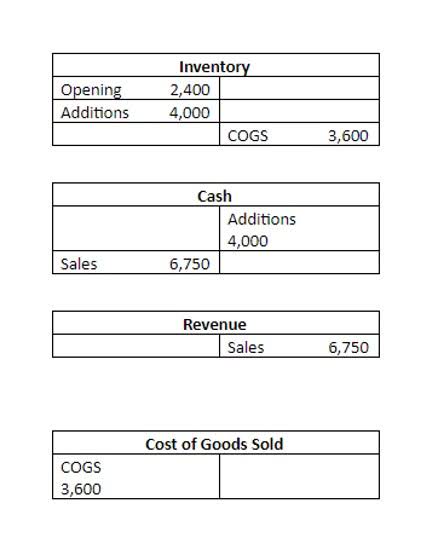
Under cash basis accounting, transactions are recorded only when cash changes hands. Rent is recognized as an expense by the tenant when paid and as revenue by the landlord when received. Current liabilities are debts that are paid in 12 months or less, and consist mainly of monthly operating debts. Examples of current liabilities may include accounts payable and customer deposits. They’re recorded in the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet. An expense represents a cost a business incurs through its operations to generate revenue, essentially the cost of resources consumed during a specific period.
- It happens primarily because they make a mistake identifying expenses with liabilities.
- Expenses refer to the costs incurred in the normal course of business operations, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and supplies.
- Understanding this distinction is important for grasping how businesses report their financial health and performance.
- Likewise, increasing assets increases equity, but a decrease in assets lowers equity.
- The payroll tax expense account shows the sum of the taxes your company owes to the IRS.
- By paying regular salaries on time, you are taking responsibility for fulfilling your obligations as a fair employer who values its workforce properly.
Liabilities vs Assets
- While Assets, Liabilities and Equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are the increases and decreases made to the various accounts whenever a financial transaction occurs.
- Another scenario where insurance can be an asset involves certain types of life insurance policies, specifically those with a “cash value” component, such as whole life or universal life insurance.
- Companies can record a payroll liability each week by debiting payroll expense and crediting payroll liability.
- Current liabilities are obligations due within one year, such as accounts payable to vendors, accrued wages owed to employees, and short-term loans.
Examples include cash, accounts receivable from customers, or a piece of machinery used in production. Liabilities are the debts, or financial obligations of a business – the money the business owes to others. Liabilities are classified as current liabilities or long-term liabilities.
- Liabilities are typically measured in monetary terms and are reported on the balance sheet, providing stakeholders with information about a company’s financial health and solvency.
- Accrued expenses theoretically make a company’s financial statements more accurate.
- You incur these when you process payroll—and will pay them at a later date.
- Liabilities are listed on a company’s balance sheet and expenses are listed on a company’s income statement.
- It involves calculating the time an employee has worked hours over a specific period.
- Assets refer to resources owned and controlled by the entity as a result of past transactions and events, from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity.
What Are Some Examples of Accrued Expenses?
Most big companies further divide the salaries payable account as per demography or department to get a clearer picture of their salary payable account. However, the company’s accrued salary expenses are the expenses that the company is expected to incur based on its best estimate. With the help of professional bookkeepers, small companies and startups can manage their https://academy.diopars.com/bookkeeper360-reviews-read-customer-service/ finances well.
SECURE TRANSACTIONS
Businesses acquire protection against potential future risks through insurance. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) generally allows businesses to deduct ordinary and necessary insurance premiums as business expenses. For example, a retail is a liability an expense business would deduct the cost of its property insurance, general liability coverage, and workers’ compensation as expenses on its income statement.